October 7, 2022 - Parul Saini, Webmedy Team
Updated Version - January 2, 2025
Loading...
Share this article on social networks
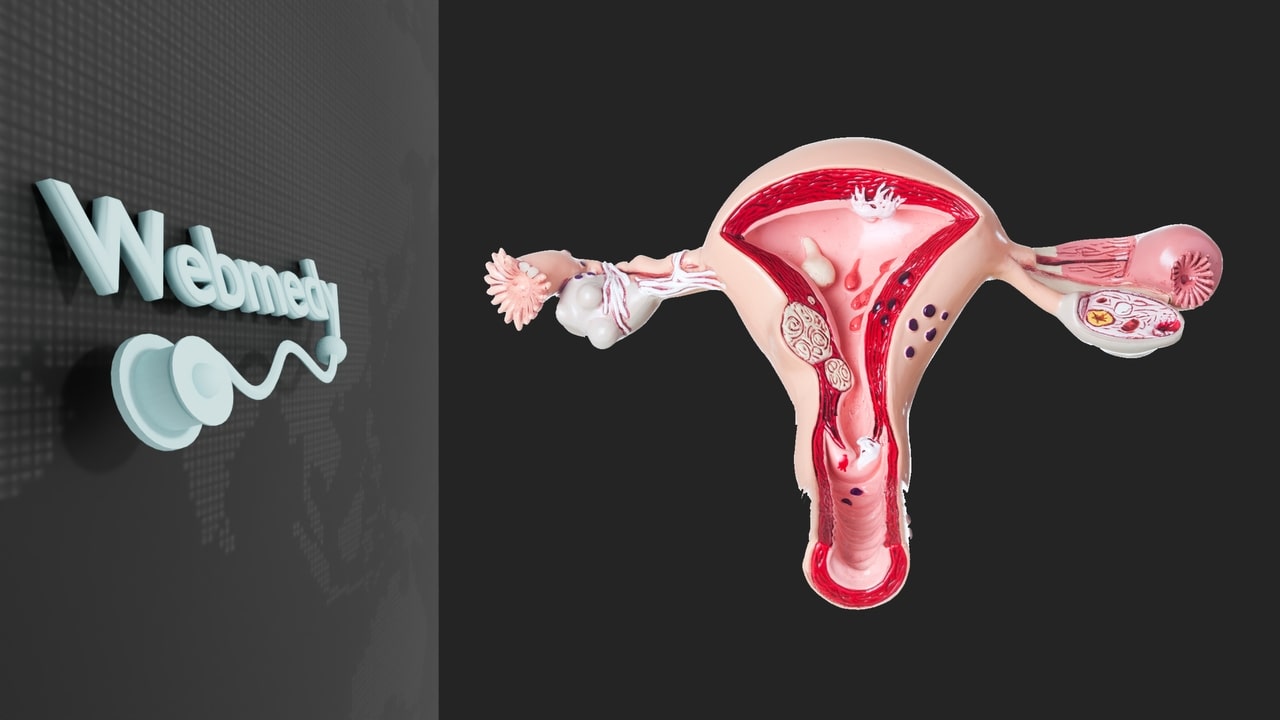
Ovarian cancer occurs when cells in the ovaries begin to multiply out of control and form tumors. If left untreated, the tumor can spread to other parts of the body. This is called metastatic ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer often has warning signs, but early symptoms are vague and easily missed.
The female reproductive system contains two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries are the size of an almond. They produce eggs (ova) as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
In this article, we will walk you through all about ovarian cancer, its symptoms, types, risks, and treatment options.
If cancer has reached a later stage without intervention, some individuals may develop the following symptoms:
If you are dealing with pleural effusion, you may experience shortness of breath, a cough, and/or chest pain.
The ovaries are made up of three types of cells. Each cell can develop into a different type of tumor:
Epithelial Ovarian Carcinomas form in the layer of tissue on the outside of the ovaries. About 85 to 90 percent of malignant ovarian cancers are epithelial ovarian tumors.
Stromal tumors grow in the hormone-producing cells. Seven percent of ovarian cancers are stromal tumors.
Germ cell tumors develop in egg-producing cells. Germ cell tumors are rare.
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown. However, these factors can increase your risk:
It's possible to have ovarian cancer without having any of these risk factors. Likewise, having any of these risk factors doesn't necessarily mean you'll develop ovarian cancer.
The treatment depends on how far cancer has spread. A team of doctors will determine a treatment plan depending on your situation. It will most likely include one or more of the following:
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms on or inside an ovary. They are common and often form during ovulation. Most ovarian cysts present little or no discomfort and are harmless.
The early symptoms of an ovarian cyst can include bloating, abdominal swelling, pain in the lower abdomen, and a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen. However, many cysts don't cause any symptoms at all.
Yes, many ovarian cysts don't cause any symptoms. They are often discovered during routine pelvic exams or ultrasounds for other health issues.
If you're experiencing symptoms, such as persistent pelvic pain, bloating, or irregular periods, consult your healthcare provider. They can confirm the presence of an ovarian cyst through an ultrasound or other imaging tests.
No, pain isn't always a symptom of an ovarian cyst. Many ovarian cysts don't cause any discomfort. However, if a cyst becomes large, it can lead to pelvic pain, bloating, or a feeling of heaviness.
Yes, some types of ovarian cysts, such as functional cysts, can cause irregular or painful periods. However, many ovarian cysts do not affect menstrual cycles.
Pain from an ovarian cyst can be dull or sharp, and it usually occurs on the side of the ovary that has the cyst. The pain may be constant, or it may come and go.
Yes, ovarian cysts can cause bloating and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. However, they are unlikely to cause significant weight changes.
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst can include sudden, sharp, severe pain on one side of the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, fever, and rapid breathing. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Yes, large ovarian cysts can press on the bladder or bowel, leading to symptoms like increased frequency of urination, difficulty emptying the bladder or bowel completely, or constipation.
Symptoms of ovarian cysts such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in menstrual cycles can mimic conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Larger cysts are more likely to cause symptoms than smaller ones. They can cause pressure, bloating, swelling, and pain in the abdomen. However, the size of a cyst does not always correlate with the severity of the symptoms.
Functional cysts, which are related to the menstrual cycle, often don't cause symptoms and typically resolve on their own. Pathological cysts, which can be benign or malignant, may grow larger and cause symptoms, but this is not always the case.
Most ovarian cysts do not affect fertility. However, certain types, such as endometriomas associated with endometriosis, or cysts caused by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can affect fertility.
Most ovarian cysts are benign and not associated with cancer. However, a small percentage of ovarian cysts can be malignant. It's important to have regular check-ups and discuss any symptoms with your healthcare provider.
Ovarian cysts are typically diagnosed through pelvic exams and imaging tests, such as ultrasounds. In some cases, blood tests may be used to evaluate the risk of ovarian cancer.
There's no sure way to prevent ovarian cysts, but regular pelvic exams can help ensure that changes in your ovaries are diagnosed as early as possible. Hormonal contraceptives can help prevent the development of new cysts.
Treatment depends on the size and type of the cyst, as well as the patient's symptoms and age. Options range from monitoring the cyst to medications, or in some cases, surgery to remove the cyst.
While there's no specific lifestyle or diet to prevent cysts, maintaining a healthy weight and balanced diet can contribute to overall health, which might reduce the risk of developing ovarian cysts.
Yes, hormonal birth control pills can help prevent the formation of new ovarian cysts. They work by preventing ovulation, which reduces the risk of developing new functional ovarian cysts.
Share this article on social networks
September 8, 2022
Although breast cancer generally shows no symptoms in the early stage, timely detection can improve your chances of beating this deadly disease. A breast lump is the most common presenting symptom. But for about 1 in 6 women with breast cancer, the broad spectrum of symptoms doesn't include a lump.
August 30, 2022
Excessive growth of male-like dark or coarse hair on a woman's face, chest, or back is due to a condition called Hirsutism. In this condition, excessive male hormones (androgens), primarily testosterone, are responsible for extra hair growth.
September 24, 2022
A group of physical and emotional symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) May occur in the days and weeks leading up to their menstrual periods, such as headaches, abdominal bloating, breast tenderness, changes in appetite, fatigue, depression, and anxiety.
Mango is a delicious tropical fruit that is not only delicious but also offers many health benefits. Mangoes are part of the family of pistachios and cashews, known as the Anacardiaceae family. Mango comes in many different varieties, each with its own unique flavor and texture.
December 10, 2022
Liver is an important organ of the body which aids in digestion, stores nutrients and detoxifies our body by eliminating harmful substances. Liver also acts as an important warrior of our immune system as it identifies harmful bacteria, viruses and toxins that enter our body, captures them and throws them out of the body. A healthy liver is essential for overall health and well being.
February 10, 2024
Imagine your body as an intricate fortress, constantly guarded by an invisible but ever-vigilant protector: mucus. This unsung hero works tirelessly, shielding you from the onslaught of environmental villains and internal turmoil. Yet, when we find ourselves constantly clearing our throats or battling with that annoying sensation of phlegm, it's a sign that our protector is working overtime. This isn't just a tale of discomfort; it's a story of resilience, a signal from our bodies that something is amiss. Let's understand this protective mechanism, exploring the myriad causes of phlegm and mucus in the throat, and uncover the ways we can support our body's natural defenses for a happier, healthier life.
February 10, 2023
Imagine a future in which medical diagnoses are made accurately and lightning-fast, and treatment plans are tailored to the individual patient. Artificial Intelligence is making such a future possible.
November 15, 2022
The healthcare industry has started adopting the Internet of Things for patient care and tracking their needs. Remote monitoring, smart sensors, medical device integration, fitness trackers, wearable biometric sensors, glucose monitors, prescription dispensers, and smart beds, are all examples of adoption of Internet of Things in healthcare.
November 8, 2022
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform healthcare. Blockchain technology can be used to build a patient-centric healthcare ecosystem that is secure and interoperable.
August 10, 2023
Are you ready to supercharge your mornings and set a healthy tone for the rest of the day? Drinking a mixture of turmeric and ginger first thing in the morning is often recommended for its potential health benefits. Consuming these two together may provide synergistic benefits while enhancing their individual effects.
January 10, 2023
Garlic has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for a variety of medical conditions. The beneficial properties of garlic are due to a compound called Allicin.
February 11, 2024
In this article, we will explore the science behind apple cider vinegar's potential to enhance weight loss efforts. From boosting metabolism and reducing fat accumulation to regulating blood sugar levels and suppressing appetite, learn how this natural remedy might support your health and fitness goals.
We all love squeezing the juice out of a lemon and savoring its inner pulp, but did you know that the peel of a lemon contains a wealth of vitamins, minerals and powerful bioactive compounds? Let's uncover the secret of lemon peel, a hidden treasure that surpasses lemon pulp in nutrient concentration.
September 12, 2022
Human growth hormone (HGH) is a hormone that promotes growth, muscle mass, and fat metabolism. HGH is a naturally occurring hormone released in the body by the pituitary gland. It can be especially important during weight loss, injury recovery, and athletic training. People can try to increase their growth hormone naturally by changing their diet and lifestyle choices.
December 11, 2023
Explore the world of cucumbers, where every bite is not just about a refreshing crunch, but also a step towards better health! Often overlooked as just a salad ingredient, cucumbers are a powerhouse of nutrients that do wonders for your body. From hydrating your skin to keeping your heart healthy, these green vegetables are full of surprises.
You might be aware of the health benefits of papaya fruit, but do you know that the green leaves of the papaya tree are a powerhouse of healing properties that have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. Papaya leaves contain a unique blend of enzymes, vitamins and antioxidants. From increasing platelet levels in dengue patients to providing relief from gastric problems, papaya leaves are a health powerhouse.
April 5, 2025
Every breath you take fuels your body with life. Your lungs can get clogged with toxins like pollution, smoke, and allergens. Thus making it harder for you to breathe and leaving you feeling sluggish. The good news is that your lungs have an incredible ability to heal and cleanse themselves. If you give them the right support, you can naturally detoxify your lungs.
Ever wondered what makes your skin glow, your joints move smoothly, or your hair stay strong? The answer often lies in two powerful proteins: collagen and gelatin. Though they come from the same source, they work in different ways—and knowing the difference can transform your health routine. Whether you're looking to boost your beauty game, heal your gut, or ease joint pain, understanding collagen vs. gelatin could be your secret weapon.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
February 16, 2025
Kidney stones are painful and can disrupt daily life. These hard mineral deposits form in the kidneys and can cause severe discomfort when passing through the urinary tract. The good news is that diet plays a key role in preventing kidney stones. By eating the right foods and avoiding harmful ones, you can lower your risk and keep your kidneys healthy. Let’s explore the best foods that help prevent kidney stones and explain why they are beneficial.
Behind every decision you make — from picking a snack to chasing a dream — there’s a powerful chemical at work: dopamine. Often called the feel-good chemical, dopamine doesn’t just make you happy — it actually helps steer your decisions every single day. Let's explore the fascinating world of dopamine and discover how it shapes the way you think, act, and choose.
February 9, 2025
Timing plays an important role in how effective an exercise routine is. Some people prefer early morning workouts, while others feel stronger in the evening. But is there really a best time to exercise?
January 31, 2025
High blood pressure is often called the silent killer because it creeps up unnoticed, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. But here’s the good news—you can take control of your health simply by making smarter food choices! The right diet can naturally lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and keep your heart strong. By focusing on nutrient-rich foods while cutting back on harmful ones, you can create a powerful defense against hypertension.
March 15, 2025
Imagine if the secret to glowing, youthful skin wasn’t in a bottle of expensive creams but hidden deep in your gut! Surprising, right? Recent research shows that the health of your gut might be the key to boosting collagen, the protein that keeps your skin firm and radiant. This gut-skin connection, known as the gut-skin axis, reveals how a happy, balanced gut can lead to clearer skin. Ready to discover how your gut and skin work together for that natural glow?
Aging has fascinated scientists for centuries. One of the most well-known theories is the Free Radical Theory of Aging (FRTA). It suggests that free radicals damage cells over time, leading to aging and disease. For decades, researchers believed that antioxidants could slow this process and extend lifespan. But is this theory still valid today? Let us explore the theory of Free Radical Theory of Aging, its rise, its decline, and what we now know about aging.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Many health problems come from nutrient deficiencies. Your body needs a variety of vitamins and minerals to function properly. When you don’t get enough, you may feel tired, weak, or even develop serious health conditions. Did you know that ou can fix most deficiencies with the right foods.Let us explore common deficiencies and the surprising foods that can help.
When it comes to gut health, probiotics and prebiotics often dominate the conversation. However, a lesser-known yet equally important player deserves recognition – postbiotics. These compounds are not merely byproducts of probiotic activity; they are powerful agents that contribute to digestive health, immune function, and much more. Get Ready to explore what postbiotics are, their unique benefits, and practical ways to incorporate them into your daily life.
December 25, 2024
mRNA vaccines have become a beacon of hope in the fight against cancer. These innovative therapies harness the power of the body's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. While these vaccines have gained fame for combating infectious diseases, their application in oncology is a game-changer.
December 23, 2024
Krill oil has gained immense popularity as a health supplement, thanks to its incredible health benefits. Extracted from tiny crustaceans called krill, this oil is packed with essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, phospholipids, and astaxanthin. Whether you're looking to boost your heart health or improve your skin, krill oil offers numerous advantages.
December 14, 2024
The liver is one of the most vital organs in your body, responsible for filtering toxins, producing bile, and regulating metabolism. A well-functioning liver is key to overall health. If you’ve been searching for the best liver detox, you’re in the right place. Let’s discover how to detox your liver naturally and improve liver health.
The relationship between kidney and blood pressure is a vital aspect of health that many people overlook. Your kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure, while high blood pressure can severely impact kidney function. This connection forms a dangerous cycle where one condition worsens the other.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Weight loss can be challenging, but did you know your body has a secret weapon? It’s called brown fat. Unlike the fat we want to lose, brown fat helps you burn calories. It works by producing heat and boosting your metabolism.
Collagen is a key protein in our bodies that keeps skin firm, joints flexible, and bones strong. As we age, collagen production naturally decreases, leading to signs of aging like wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin. But the good news is there are ways to boost collagen production naturally!
Inflammation is a major cause of joint pain and stiffness, particularly for those with arthritis or other joint-related issues. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet is a natural way to manage and reduce inflammation, improve flexibility, and support overall joint health. Certain foods can fight inflammation and promote joint flexibility, while others may worsen inflammation. Let’s understand which are the best foods to include, foods to avoid, plus lifestyle habits and supplements that can further support joint health.
Water is the source of life, but are you drinking it right? Believe it or not, you can make mistakes with something as simple as drinking water. If you make these mistakes, you could be missing out on the incredible health benefits of water. Worse yet, it can harm your body.
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a debilitating condition characterized by persistent fatigue that doesn't improve with rest. It affects millions of people worldwide and can severely impact daily life. Understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial for those struggling with chronic fatigue. Let’s explore the common causes of chronic fatigue, foods that can help combat chronic exhaustion, and effective supplements to support energy levels. By addressing these factors, you can find relief from chronic fatigue syndrome symptoms and discover potential chronic fatigue treatment options that work for you.
October 2, 2024
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, affects millions of people around the world. If not managed it can cause serious health problems. But here's the good news—changing your diet can help lower your blood pressure naturally. Let's learn about the top foods that can make a big difference in reducing high blood pressure naturally.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
September 25, 2024
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition affecting many people worldwide. It occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. This backflow, known as acid reflux, can irritate the esophageal lining, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms.
July 29, 2024
Dark circles under the eyes can make you look tired and older than you feel, casting shadows on your vibrant personality. Whether they caused from sleepless nights, genetic factors, or the stresses of daily life, they are a common beauty concern.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, especially among women, and can cause significant discomfort and pain. While it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for severe or recurrent UTIs, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and support the healing process.
Sesame seeds have been a staple in many cuisines for centuries. These tiny seeds are not only flavorful but also packed with nutrients. From boosting heart health to enhancing skin and hair, sesame seeds are a true superfood. Let’s explore the health benefits of sesame seeds, how to use them, and why they deserve a spot in your daily diet.
July 27, 2024
Are you pushing your limits at the gym but feeling constantly sore and fatigued? Achieving your fitness goals isn't just about lifting heavier or running faster - it's also about how well you recover. Effective muscle recovery can boost your performance, prevent injuries, and ensure that you’re always ready to tackle your next workout.
November 24, 2024
Persimmons, often called the fruit of the gods, are more than just a sweet, vibrant treat. They are a powerhouse of nutrition with incredible health benefits. From boosting heart health to giving your skin a radiant glow, this delicious superfruit deserves a spot in your daily diet. Packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, persimmons can transform your health in ways you never imagined.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Peppermint oil, derived from the peppermint plant, has been a cherished remedy in traditional medicine for centuries. Its primary component, menthol, is the secret behind many of its powerful health benefits.
November 14, 2024
Coconut water, the clear liquid inside young coconuts, is more than just a refreshing drink. With its slightly sweet, nutty taste and rich nutrient profile, coconut water has gained popularity for its unique health benefits. Packed with electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and calcium, it’s an ideal drink for hydration and natural wellness.
Alzheimer's disease and muscle fatigue may seem like unrelated conditions at first glance, but emerging research suggests a surprising link between them: inflammation. Understanding this connection could pave the way for new treatment approaches and improve the quality of life for those affected.
November 6, 2024
Oats are more than just a popular breakfast food; the benefits of oats are numerous and diverse. Oats have gained recognition for its exceptional nutritional profile and its potential to enhance overall health. Let’s explore the incredible oats health benefits, including how oats can improve heart health, support digestion, and even help with weight management. By understanding the full range of oatmeal benefits, you can see why incorporating oats into your diet is a smart choice.
July 24, 2024
When it comes to heart health, the tiny aspirin tablet might just be one of the most powerful friend in your medicine cabinet. Long known for its ability to soothe aches and pains, aspirin also plays a crucial role in protecting your heart. Let us discover how this everyday medication could be a game-changer for your cardiovascular well-being.
Liquid biopsies represent a revolutionary advancement in cancer detection and monitoring. By analyzing tiny fragments of DNA and other biomarkers in the blood, liquid biopsies offer a non-invasive, real-time glimpse into the presence and progression of cancer. This revolutionary method promises not only earlier detection but also a more personalized approach to treatment.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
July 23, 2024
Eucalyptus oil is quite a versatile aromatic oil that offers several benefits. Whether you’re looking to breathe easier, relieve pain, or simply uplift your mood, eucalyptus oil offers several benefits that can transform your daily routine.
October 17, 2024
Dragon fruit, also known as pitaya, is a vibrant fruit with plenty of health benefits. This tropical fruit has gained popularity worldwide for its striking appearance and powerful nutritional profile. Let’s explore the top dragon fruit benefits and why you should consider adding this superfruit to your diet. Whether you prefer the red dragon fruit or the yellow variety, dragon fruit offers something for everyone.
July 23, 2024
Vicks VapoRub is a popular topical ointment that has been used for generations to provide relief from various ailments. This multipurpose ointment isn't just for soothing colds and coughs; it's a versatile remedy that can ease muscle aches, relieve headaches, and even tackle skin issues.
July 22, 2024
From preventing painful fractures to warding off osteoporosis, understanding and maintaining your bone density is key to staying vibrant and mobile as you age. High bone density is essential for a healthy, active life.
IoT offers significant benefits for chronic disease management by enabling continuous monitoring of patients' health metrics. With devices like smart glucose monitors and blood pressure cuffs, healthcare providers can receive real-time data. This allows for timely interventions, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient engagement, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
In the fight against cancer, traditional chemotherapy has long been a cornerstone of treatment. However, as science advances, a new era of non-invasive therapies is emerging, offering promising alternatives that could transform cancer care.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
July 21, 2024
Imagine tackling that nagging back pain or persistent headache not with synthetic drugs, but with the powerful, time-tested remedies found in your own kitchen or garden. Whether you're looking for a natural alternative for pain relief or just curious about holistic wellness, these remedies might just be your solution.
Imagine a future where aging is not just slow decline, but a process we can actively control and delay. Imagine a world where our bodies stay young and flexible, not just by chance, but through cutting-edge science. Scientists are uncovering the mystery of how protein inhibition could revolutionize our understanding of aging. By targeting specific proteins that induce cellular damage and degradation, we may be able to stop the biological clock.
September 22, 2024
Did you know that the sugar in your diet could be secretly damaging your skin? Although sugar may be a delicious thing, it can wreak havoc on your complexion. Not only does sugar cause acne but also accelerates the development of wrinkles, sugar has a huge impact on your skin health. Let's understand how sugar affects your skin, how cutting down on sugar can be an anti-ageing remedy - and all this naturally.
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing technology that's making significant strides in cancer research. This technology offers the potential to rewrite cancer’s genetic code, opening doors to targeted therapies and personalized treatments that could transform how we approach one of the most formidable diseases.
July 31, 2024
Honey, a natural wonder, isn't just for sweetening your tea; it's a powerful, all-natural skincare hero. From moisturizing and healing to brightening and anti-aging, honey offers many benefits that can transform your complexion.
Are you struggling with weight management or diabetes? GLP-1 drugs, like Wegovy and Zepbound, not only help control blood sugar levels but also offer a promising solution for weight loss.
Stay Informed on Health and Wellness
Get access to award-winning industry coverage, including latest news, case studies and expert advice.
Subscribe to Webmedy Youtube Channel for Latest Videos
Donate
Your generous donation makes a huge difference!
Loading...

Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Stay Informed on Health and Wellness
Get access to award-winning industry coverage, including latest news, case studies and expert advice.
Subscribe to Webmedy Youtube Channel for Latest Videos
Donate
Your generous donation makes a huge difference!